Table of Contents
Structural and Functional Imaging Techniques:
Typical Pulse Sequences at 3T
Overview of the BIAC 3T Scanner The 3 Tesla (3T) scanner contains a short-bore magnet with an active shield. The scanner uses a twin-gradient system, providing a 2.2 G/cm gradient for high-linearity imaging in body or large field of view (FOV) scans and a 4 G/cm gradient for a high-slew rate in fast imaging. The scanner also contains a parallel imaging infrastructure with an 8-channel head coil, with the option to upgrade to 16 channels.
Structural Imaging Techniques
There are several main types of structural imaging techniques: T1 Imaging, Proton Density, T2 Imaging, and Diffusion Tensor Imaging.
- SENSE
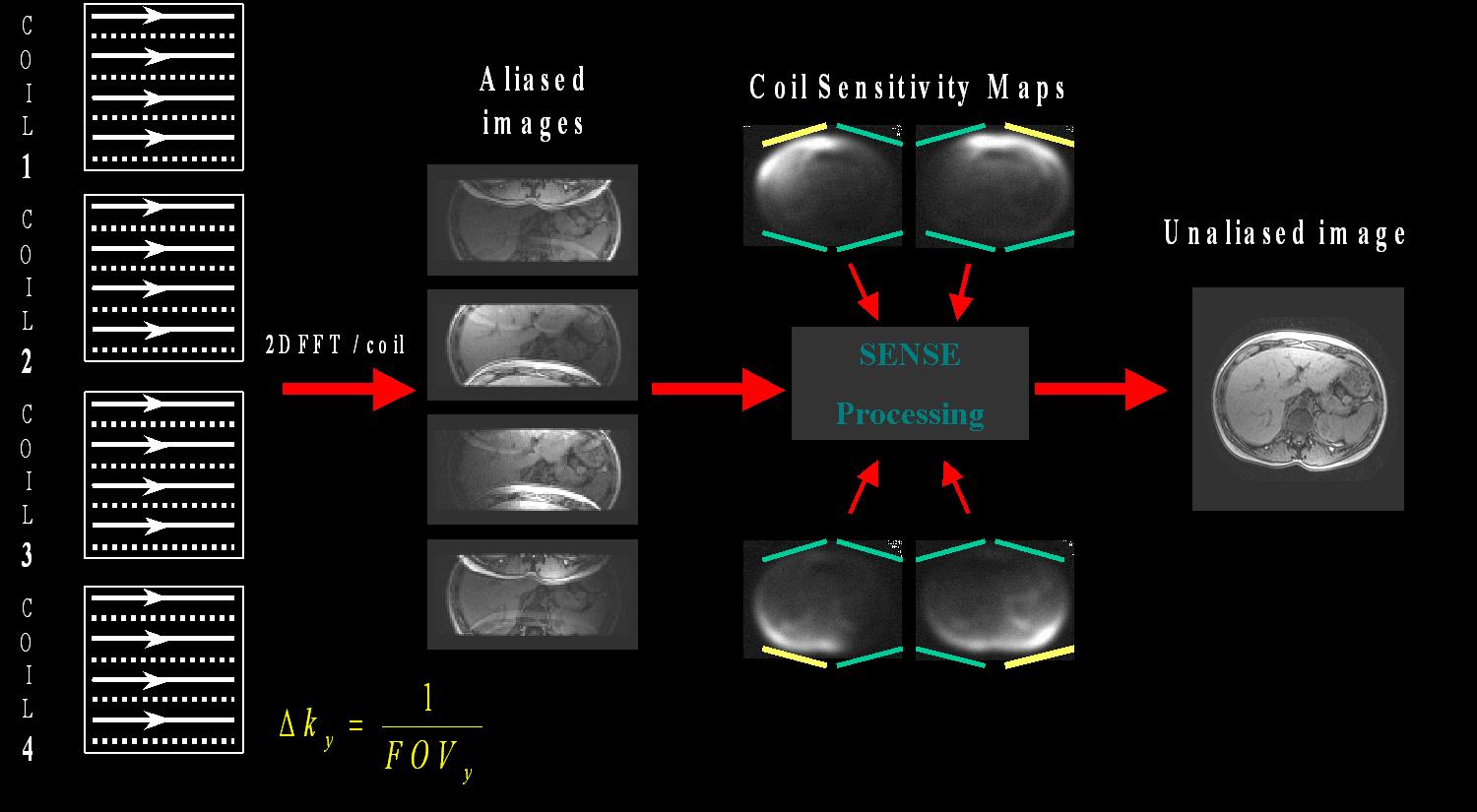
To understand the two types of T1 Imaging available with the 3T scanner, we must first understand SENSE. Sensitivity Encoding, or SENSE, uses multiple coils to retrieve images of different sections of the brain and compile them into a single parallel image.
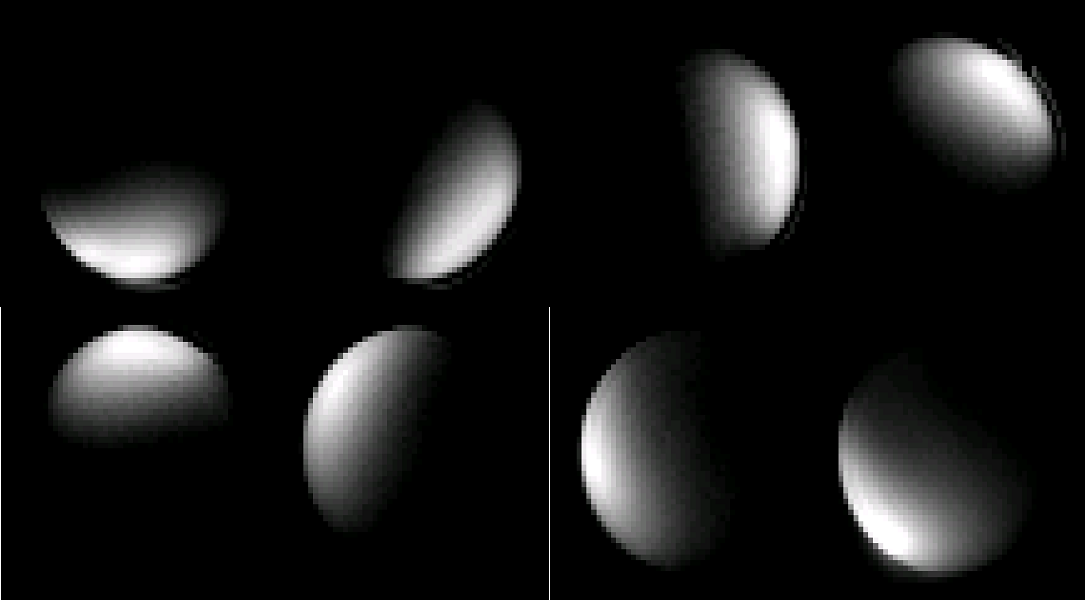
- Individual Coil Sensitivity of Our 3T
- T1 Imaging
T1 Imaging provides information about the relative T1 values of tissue. T1 Imaging involves 3D Fast Spoiled Gradient Recalled (SPGR) acquisition with Intensity Normalization. The typical imaging parameters for 3D FSPGR acquisition are as follow:- Inversion-prepared (TI = 450 ms)
- TR 22 ms, TE 5.4 ms, flip angle 20°
- imaging matrix 2562, FOV 25.6 cm,
- slice thickness 1 mm
- Imaging time: 4 min
3D FSPGR acquisition can be done with or without using SENSE.
- 3D FSPGR with SENSE
3D FSPGR Imaging with SENSE allows for two times as fast imaging speed and better spatial coverage, but has a lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
* 3D FSPGR without SENSE
3D FSPGR Imaging without SENSE allows for better SNR, but has some signal loss at the edge of the images.
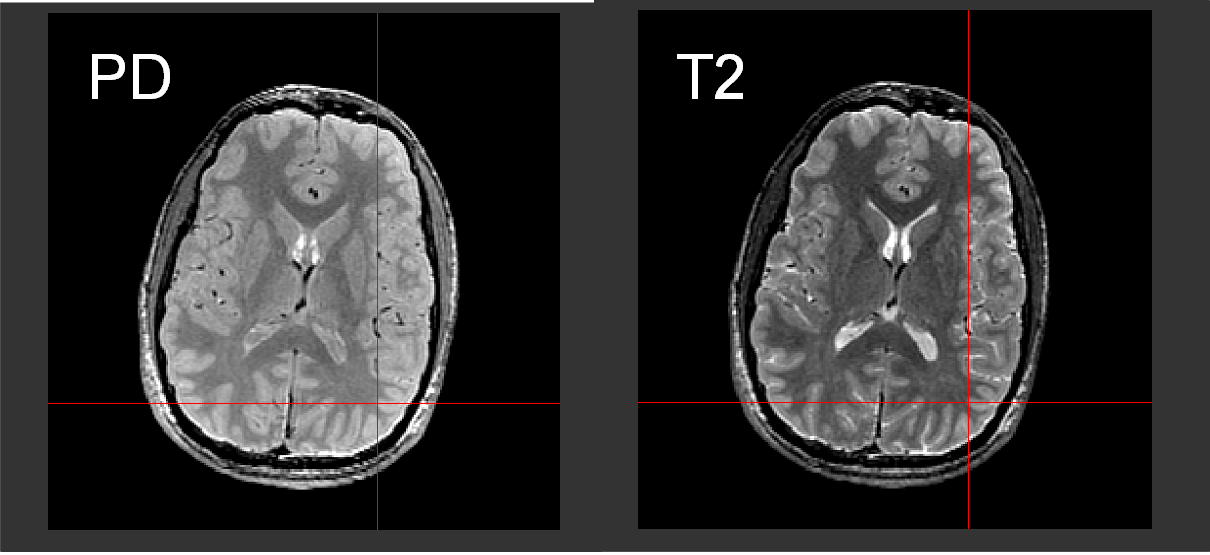
- Proton-Density and T2 Imaging
Proton-Density Imaging creates MR images that are sensitive to the number of protons present within each voxel. T2 Imaging, on the other hand, provides information about the relative T2 values of tissue. Using the 3T Scanner, Proton-Density and T2 Images are acquired using a 2-D Fast Spin Echo with Intensity Normalization. The typical imaging parameters for 2D FSE acquisition are as follow:- 2D Fast Spin Echo (FSE),
- Dual echo times at 30 ms (PD) and 75 ms (T2)
- 1x1x1 mm isotropic resolution
- Imaging time: dual contrast – 9 min, T2 only – 5 min
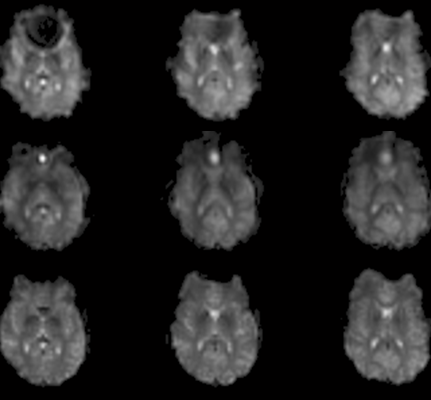
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) collects images that provide information about the magnitude and direction of molecular diffusion. With SENSE acquisition, DTI now sees low distortion, high SNR, and large spatial coverage. The typical imaging parameters for DTI are as follow:- 128 x 128 single-shot EPI
- 15 non-collinear encoding directions
- b factor of 1000 s/mm2
- 8-channel SENSE acquisition
- 2 x 2 x 2 mm isotropic resolution
- under 5 min total imaging time
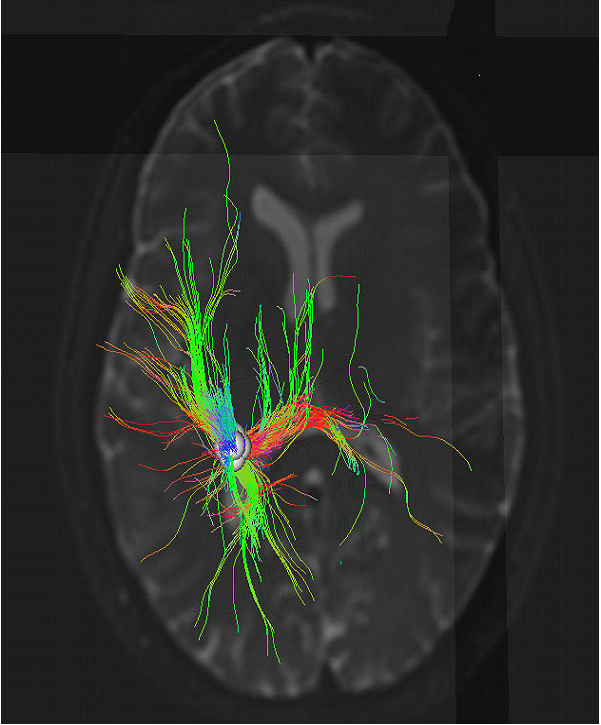
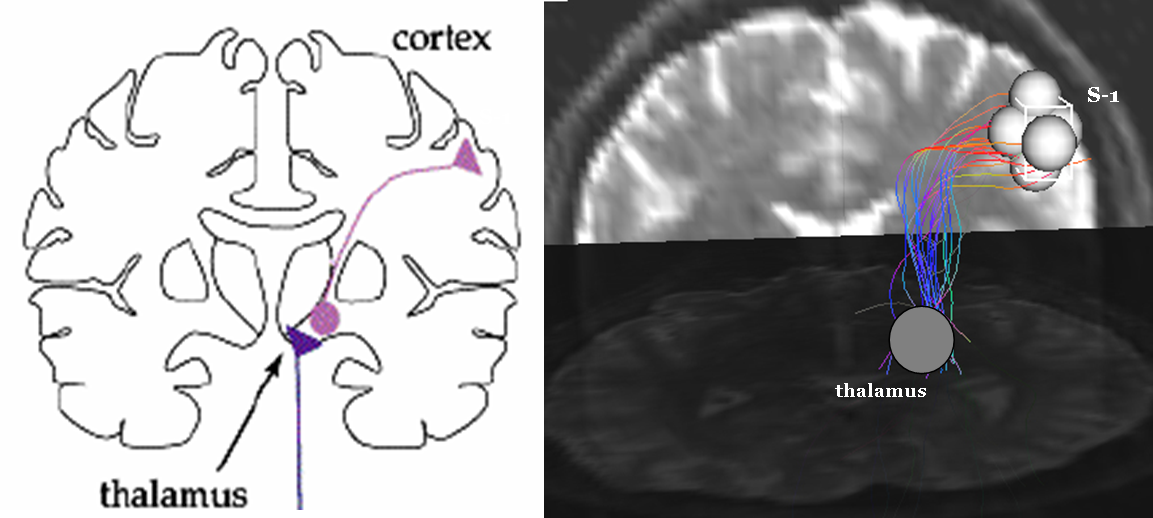
DTI is often used to create maps of fractional anisotropy. Compiling these images allows for the measurement of relative motion of water molecules within the voxel, providing maps of fiber tracking between regions.
- Region Based Fiber Tracking
- Thalamocortical Projection (Tracking Between Regions)
Functional Sequences on the 3T
Functional Sequences on the 3T were developed in-house at BIAC. Functional sequences are designed to map out patterns of activity in different regions of the brain. BIAC built functional sequences upon the spiral waveform originated from Stanford (Dr. Gary Glover) and EPI waveform originated from MCW (Dr. Eric Wong at UCSD). Spiral imaging is a technique for fast image acquisition that uses sinusoidally changing gradients to trace a corkscrew trajectory through k-space. K-space is a notation scheme used to describe MRI data. Echo-planar imaging, EPI, is a technique that allows for the collection of an entire two-dimensional image by changing spatial gradients rapidly following a single electromagnetic pulse from a transmitter coil. Functional sequences on the 3T are capable of high throughput using spiral-in, spiral-out, and EPI techniques, with spiral-in at 24 frames per second (f/s) (use < 20 f/s to reduce gradient heating), spiral-out at 17 f/s, and EPI at 17 f/s. EPI has been modified to accommodate navigator echoes in order to remove ghosting artifacts from gradient imperfection and center frequency drift that were mostly due to gradient heating at high throughput.
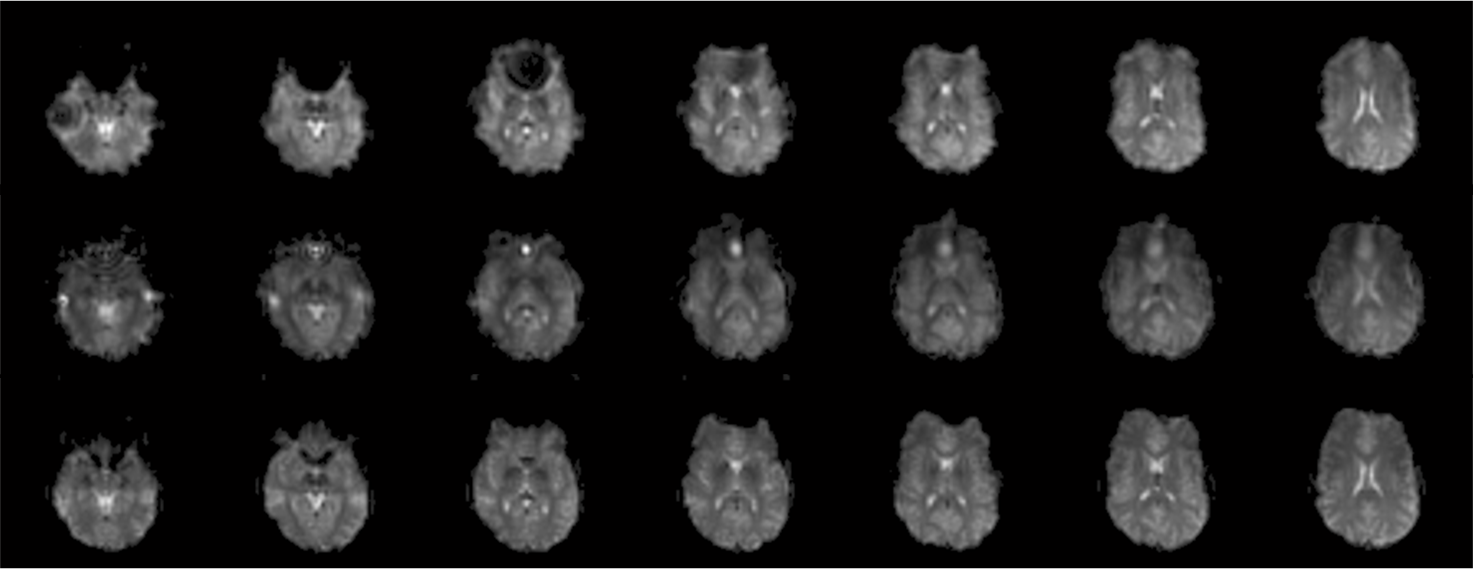
- Eight-Channel Spiral-Out Imaging
Spiral-Out Imaging is the most common form of spiral imaging. It follows a corkscrew path that beings at the center of the k-space and ends at the periphery.
- Eight-Channel Spiral-In Imaging
Spiral-In Imaging, on the other hand, follows a corkscrew path that beings at the periphery of k-space and ends at the center.
- Eight-Channel EPI Imaging
As stated previously, Echo-Planar Imaging, EPI, allows for the collection of an entire two-dimensional image by changing spatial gradients rapidly following a single electromagnetic pulse from a transmitter coil.
- Spiral-Out vs. Spiral-In vs. EPI
Functional Sequence Summary
Each of these techniques has its advantages and its disadvantages:
- The Spiral-Out technique is capable of very short TE (Echo time) and is used for perfusion imaging in arterial spin labeling technique. In addition, it has more room to accommodate the diffusion gradients used in diffusion imaging. However, spiral-out imaging has a large signal dropout at the ventral brain regions and a low internal contrast.
- The Spiral-In technique has better signal recovery at the ventral brain region than the spiral-out technique, and it is capable of high throughput. Spiral-in imaging, however, has blurry edges and low internal contrast.
- EPI allows for both high internal contrast and clear image edges, but it has spatial distortions at the ventral and frontal brain regions, along with some signal losses.